
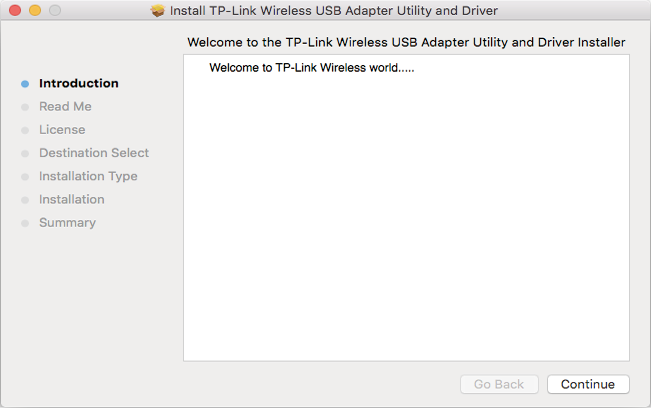
- #Usb menu chapter for mac how to
- #Usb menu chapter for mac install
- #Usb menu chapter for mac drivers
Of course, when it comes to using a newer MacBook, like the MacBook Pro or MacBook Air, you're going to want it to come with a USB-C port unless you have a USB-C hub. Plus, its ultrafine 4K display and high color fidelity make this screen look amazing right out of the box. With one Thunderbolt 3 port, USB-A, an HDMI, and multiple DisplayPort ports, this monitor has tons of connectivity to attach all your favorite devices. Use of livecd-iso-to-disk on any distribution other than Fedora is unsupported and not expected to work: please use an alternative method, such as Fedora Media Writer.LG's big 34-inch 32UL950 is not only a Thunderbolt 3 monitor, meaning you can daisy chain monitors together but also has quite a few ports. Even if it happens to run and write a stick apparently successfully from some other distribution, the stick may well fail to boot. Livecd-iso-to-disk is not meant to be run from a non-Fedora system. livecd-iso-to-disk on other Linux distributions
#Usb menu chapter for mac install
If your test boot reports a corrupted boot sector, or you get the message MBR appears to be blank., you need to install or reset the master boot record (MBR), by passing -reset-mbr when writing the stick. If you get this message from fdisk, you may need to reformat the flash drive when writing the image, by passing -format when writing the stick. Partition has different physical/logical endings If you get the message Need to have a filesystem label or UUID for your USB device, you need to label the partition: dosfslabel /dev/sdX LIVE. Information: Don't forget to update /etc/fstab, if necessary. Number Start End Size Type File system Flagsġ 32.3kB 1062MB 1062MB primary fat16 boot Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
#Usb menu chapter for mac drivers

#Usb menu chapter for mac how to

Performing administration tasks using sudo.Configuring networking with NetworkManager CLI (nmcli).Disabling the GNOME automatic screen locking.Setting a key shortcut to run an application in GNOME.Configuring Xorg as the default GNOME session.Configuring X Window System using the nf file.Installing Chromium or Google Chrome browsers.Installing plugins for playing movies and music.APT command equivalents on Fedora with DNF.Securing the system by keeping it up-to-date.Adding or removing software repositories in Fedora.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
